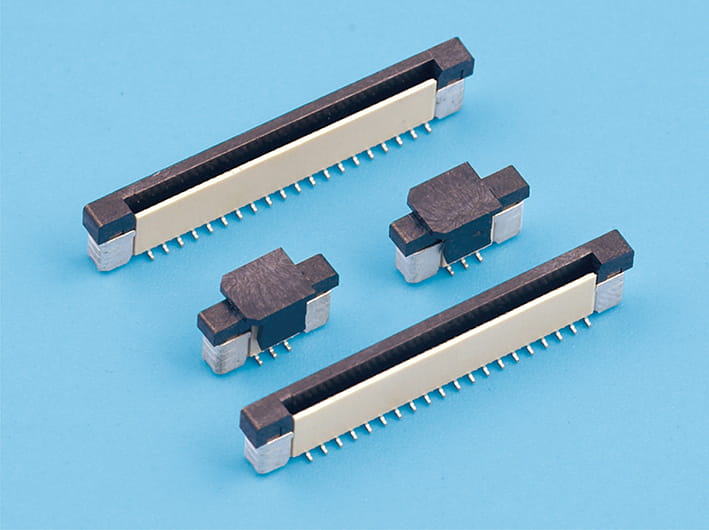
The Impact of Signal Transmission Speed in Board to Board Power Connectors
China Wholesale Board to Board Power Connector Producer
The speed at which signals are transmitted through a Board to Board Power Connector is a key performance metric that has significant implications for the operation of electronic devices. These connectors are the backbone of communication within complex electronic systems, and their ability to facilitate rapid signal transfer is crucial for the overall performance and efficiency of the devices they are a part of. This article will explore the various factors that influence the signal transmission speed of Board to Board Power Connectors and how these factors can affect the functionality of the devices that rely on them.
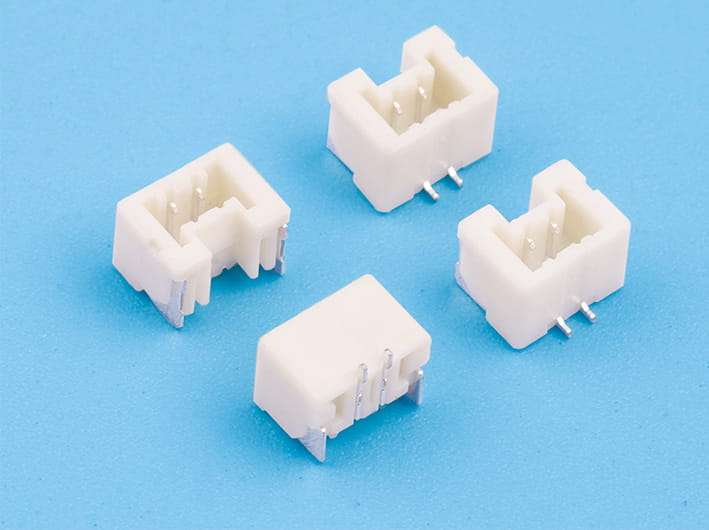
In modern electronics, the demand for increased data transfer rates has led to a greater focus on the capabilities of Board to Board Power Connectors. These connectors are not only responsible for the power supply but also for the transmission of data signals between different components of a system. The speed of signal transmission through these connectors is influenced by several factors, including the materials used, the design of the connectors, and the overall system architecture.
One of the primary materials used in the construction of Board to Board Power Connectors is the metal alloy from which the contacts are made. Gold-plated contacts are often preferred due to their good conductivity and resistance to corrosion, which can help maintain a consistent signal transmission speed over time. However, the thickness of the plating and the quality of the plating process can also impact the speed at which signals are transmitted.
The design of the Board to Board Power Connectors is another critical factor that affects signal transmission speed. Connectors with a higher pin count can potentially allow for more parallel signal paths, which can increase the overall data transfer rate. However, this also increases the complexity of the connector and the potential for crosstalk between signals, which can degrade the signal integrity. Additionally, the geometry of the connector and the alignment of the pins can impact the signal transmission speed, with misalignments causing increased resistance and slower signal propagation.
The system architecture also plays a role in determining the signal transmission speed of Board to Board Power Connectors. In systems where the connectors are part of a high-speed data bus, the overall design must accommodate the high-frequency signals without significant signal degradation. This may involve the use of shielded connectors to reduce electromagnetic interference or the incorporation of signal integrity enhancement features such as impedance matching.
As technology continues to advance, the demand for faster signal transmission speeds through Board to Board Power Connectors is only increasing. This is particularly true in applications such as high-performance computing, where the speed of data transfer can be a critical factor in overall system performance. Engineers must carefully consider the materials, design, and system architecture when selecting or designing Board to Board Power Connectors to ensure that they can meet the demands of the application.
In conclusion, the signal transmission speed of Board to Board Power Connectors is a multifaceted issue that involves a careful balance of materials, design, and system architecture. By understanding the factors that influence the speed of signal transmission, engineers can design connectors that meet the rigorous demands of modern electronics. As the need for faster data transfer rates continues to grow, the performance of Board to Board Power Connectors will remain a critical area of focus in the field of electronic engineering.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español عربى
عربى