Evaluating BTB Connector Performance Under Vibration Stress
Introduction to BTB Connector
Definition and Purpose: A BTB Connector is a type of electrical connector designed to link two printed circuit boards (PCBs) directly.
Common Applications: Widely used in industrial electronics, automotive electronics, consumer devices, and communication equipment.
Importance of Mechanical Reliability: In high-performance and mobile systems, connectors must withstand vibrations and shocks to ensure consistent electrical connections.
Structural Design and Mechanical Strength
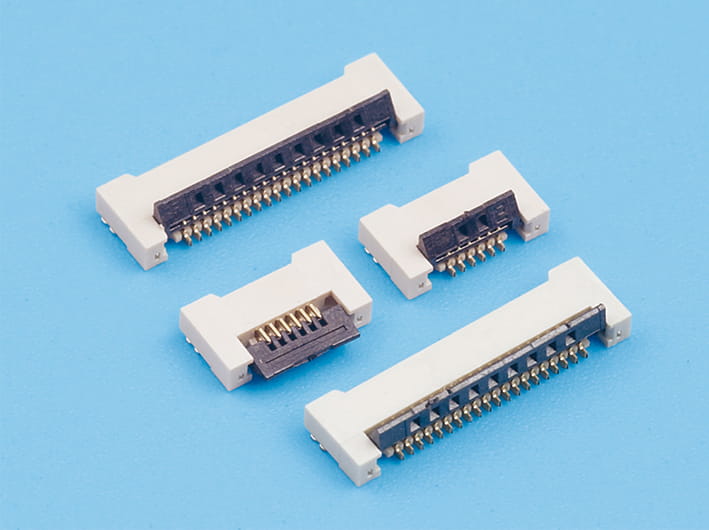
Pin and Socket Construction:
- BTB Connectors use multiple pins and sockets arranged in a compact format.
- The design allows for a secure mating that resists loosening under moderate vibration.
Housing Material:
- Insulating materials such as LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer) or reinforced plastics provide durability.
- High-strength materials improve resistance to mechanical shock and deformation.
Locking Mechanisms:
- Some BTB Connectors incorporate latch or friction-fit designs.
- These features enhance retention force, preventing accidental disengagement during vibration or impact.
Vibration Resistance Performance
- Mechanical Testing Standards:
BTB Connectors are often tested according to IEC 60068-2-6 or similar vibration standards.
Tests simulate harmonic, sinusoidal, and random vibrations that devices may experience during operation.
- Factors Influencing Vibration Resistance:
Pin Density and Size: Denser connectors may better distribute mechanical stress.
Connector Length: Shorter connectors are less prone to bending and flexing under vibration.
Mating Force: Proper insertion depth ensures pins remain engaged even under high-frequency vibrations.
- Failure Modes:
Repeated vibration may cause contact wear or intermittent connectivity if the design is insufficient.
Using reinforced pins and precise tolerances reduces these risks.
Mechanical Shock Resistance
1. Shock Testing Standards:
BTB Connectors are evaluated under IEC 60068-2-27 or MIL-STD-202 for mechanical shocks.
Testing simulates sudden drops, impacts, or acceleration forces during transport or operation.
2. Design Considerations:
- Housing Rigidity: Stiffer housings absorb and distribute impact energy.
- Contact Retention: Springs or compliant contacts maintain electrical continuity even under sudden forces.
- PCB Mounting: Surface-mount or through-hole soldering techniques enhance connector stability on the board.
3. Impact on Electrical Performance:
Properly designed BTB Connectors maintain low contact resistance and signal integrity during and after shocks.
High-quality materials prevent micro-cracks or deformation that could cause failures.
Environmental and Operational Factors
Temperature Effects:
Thermal expansion and contraction can influence the connector’s resistance to vibration.
High-temperature-rated materials reduce the risk of loosening or material fatigue.
Humidity and Contamination:
Dust, moisture, or corrosive environments may reduce mechanical and electrical reliability.
Sealed or coated connectors improve performance under harsh conditions.
Repeated Mating Cycles:
Connectors must maintain vibration and shock resistance even after multiple insertions and removals.
Using high-quality plating (gold or tin) on contacts improves durability over repeated use.
Applications Where Vibration and Shock Are Critical
Automotive Electronics:
- Vehicles experience constant vibration and occasional impacts.
- BTB Connectors in engine control units, infotainment, and ADAS modules must withstand these stresses.
Industrial Machinery:
- Heavy equipment generates vibration during operation.
- Reliable connectors prevent downtime due to intermittent connections.
Consumer Electronics:
- Portable devices like laptops or handheld tools can drop or experience shocks.
- Compact BTB Connectors maintain signal integrity while decreasing mechanical failures.
- BTB Connector demonstrates strong potential in environments with vibration and mechanical shocks when designed and manufactured properly.
- Factors such as housing material, pin retention, connector length, and mating force significantly influence durability.
- Environmental conditions and operational stress must also be considered to ensure long-term reliability.
As devices continue to become more compact and mobile, selecting BTB Connectors with verified vibration and shock resistance is essential to maintain both electrical performance and mechanical stability.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español عربى
عربى