Ensuring Compatibility With Various FPC Flat Connectors
Understanding FPC Flat Connectors
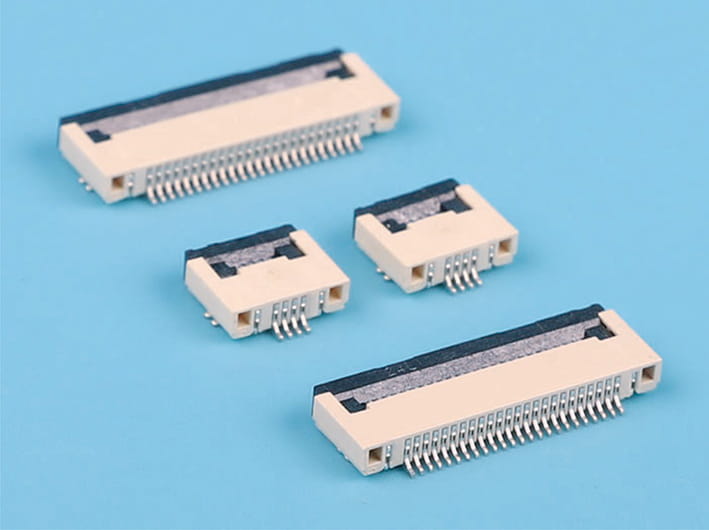
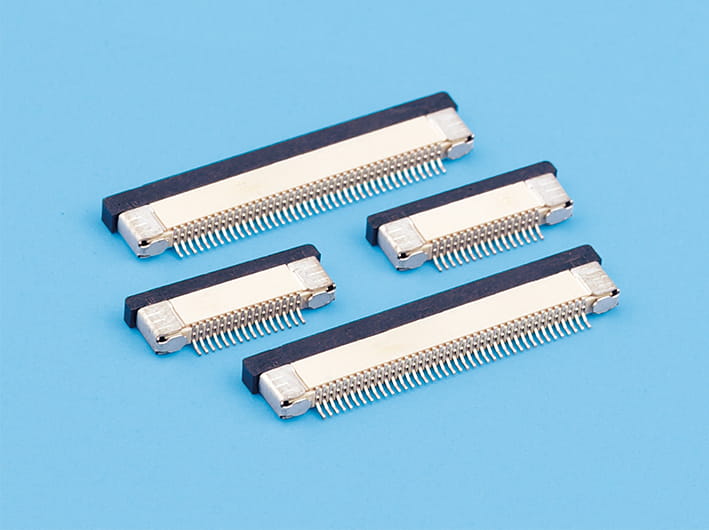
Definition and Function: FPC flat connectors are specialized electrical connectors designed for flexible printed circuits (FPCs). They provide a compact, reliable, and low-profile interface between flexible cables and printed circuit boards.
Applications: Widely used in mobile devices, laptops, cameras, automotive electronics, and other compact electronic systems where space constraints are critical.
Importance of Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility with different FPC thicknesses is essential for maintaining signal integrity, mechanical reliability, and overall device performance.
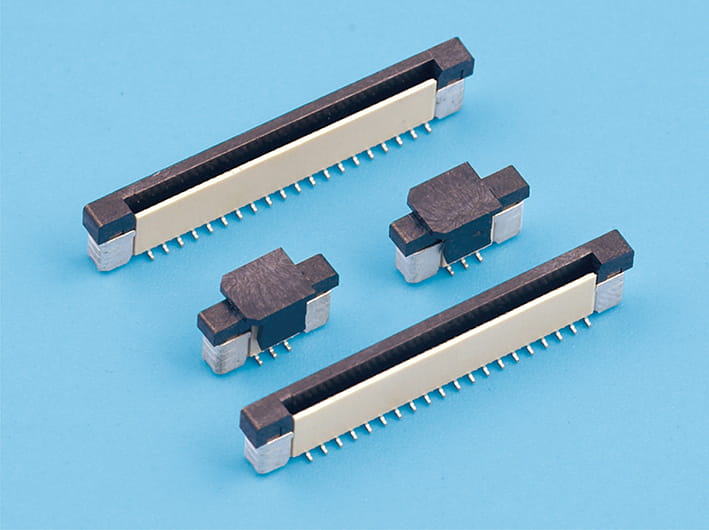
Factors Affecting Compatibility
Connector Pitch and Design:
- The pitch, or spacing between contacts, must align precisely with the FPC conductor pattern.
- Adjustable or multi-range connector designs can accommodate variations in FPC thickness.
Contact Pressure:
- Proper contact pressure is crucial to ensure reliable electrical connectivity.
- Too much pressure can damage thin FPCs, while insufficient pressure may cause intermittent connections in thicker FPCs.
Insertion Depth and Retention:
- The connector must securely hold FPCs of varying thickness without causing deformation or loose connections.
- Locking mechanisms or sliders are often used to maintain consistent retention.
Challenges With Different FPC Thicknesses
Thin FPCs:
- Very thin FPCs may not provide enough rigidity, increasing the risk of bending or misalignment during insertion.
- The connector must apply gentle yet reliable pressure to avoid damaging the traces.
Thick FPCs:
- Thicker FPCs may require wider contact slots or higher insertion force, which can strain the connector structure if not designed for flexibility.
- Ensuring even contact across all pins becomes critical to prevent open circuits or signal degradation.
Tolerance Variations:
Manufacturing tolerances in both connectors and FPCs can affect fit, requiring connectors with adjustable or flexible contacts.
Design Solutions for Multi-Thickness Compatibility
- Flexible Contact Design:
Spring-loaded contacts or compliant metal terminals allow connectors to accommodate a range of FPC thicknesses while maintaining consistent pressure.
- Locking and Latching Mechanisms:
Sliding locks, flip locks, or latch systems help secure FPCs of different thicknesses without overstressing the material.
- Standardized and Adjustable Models:
Some connectors are manufactured with adjustable slots or multi-thickness specifications to support various FPC designs without compromising performance.
Testing and Verification
Mechanical Testing:
- Simulating repeated insertions ensures the connector can handle thin and thick FPCs without damage.
- Mechanical tests also verify that retention force remains consistent across thickness ranges.
Electrical Testing:
- Continuity and signal integrity tests ensure that variations in FPC thickness do not compromise performance.
- High-frequency or high-speed testing is particularly important for connectors used in data-intensive applications.
Environmental Testing:
Temperature cycling, vibration, and humidity tests help verify that the connector maintains reliable contact under real-world conditions.
Installation Practices
- Proper Alignment:
Carefully align the FPC with the connector to prevent misalignment or pin damage.
- Gentle Insertion Force:
Avoid excessive pressure when inserting thin FPCs to prevent tearing or bending.
- Consistent Handling:
For connectors supporting multiple thicknesses, always follow manufacturer guidelines to ensure reliable and long-lasting connections.
Benefits of Using Multi-Thickness Compatible Connectors
- Versatility: One connector model can handle multiple FPC designs, reducing inventory complexity and cost.
- Reliability: Properly designed connectors prevent open circuits, intermittent contacts, and mechanical failure.
Ease of Maintenance and Replacement:
Devices using standardized multi-thickness connectors are easier to repair or upgrade without custom components.
Compatibility with varying FPC thicknesses is a critical feature of modern FPC flat connectors. By considering contact design, locking mechanisms, tolerance allowances, and proper installation, manufacturers can ensure reliable electrical and mechanical performance. A well-engineered FPC Flat Connector supports multiple FPC thicknesses without compromising signal integrity, durability, or usability. Proper testing, material selection, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines further enhance reliability, making these connectors indispensable for compact and high-performance electronic devices.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español عربى
عربى